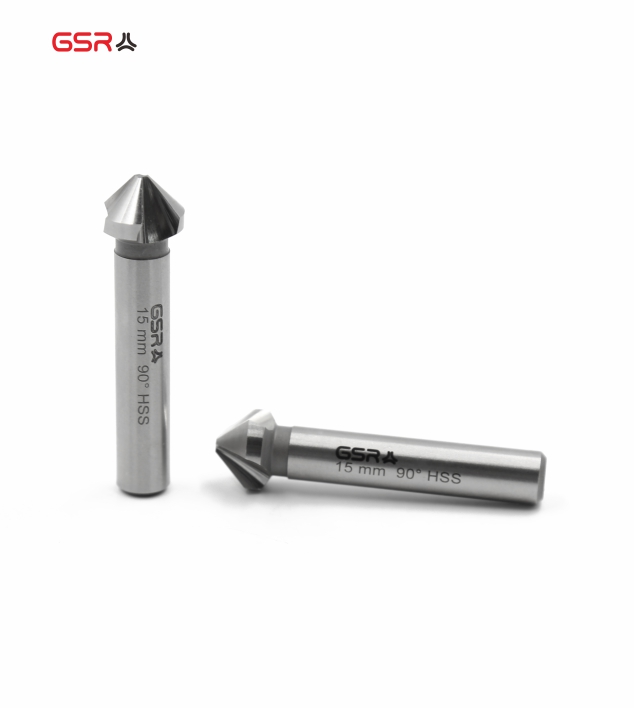
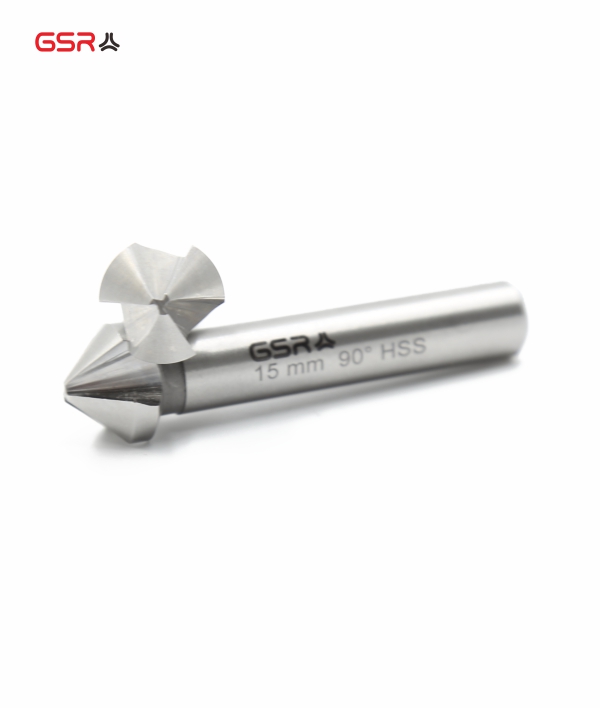
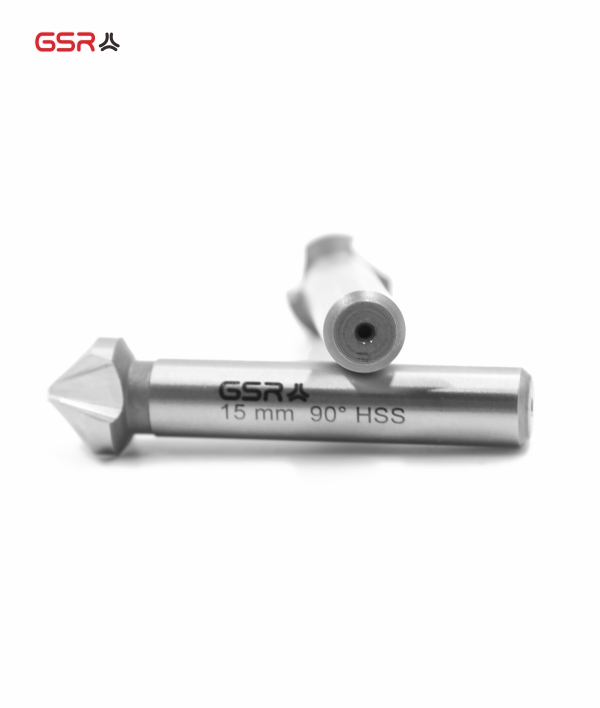
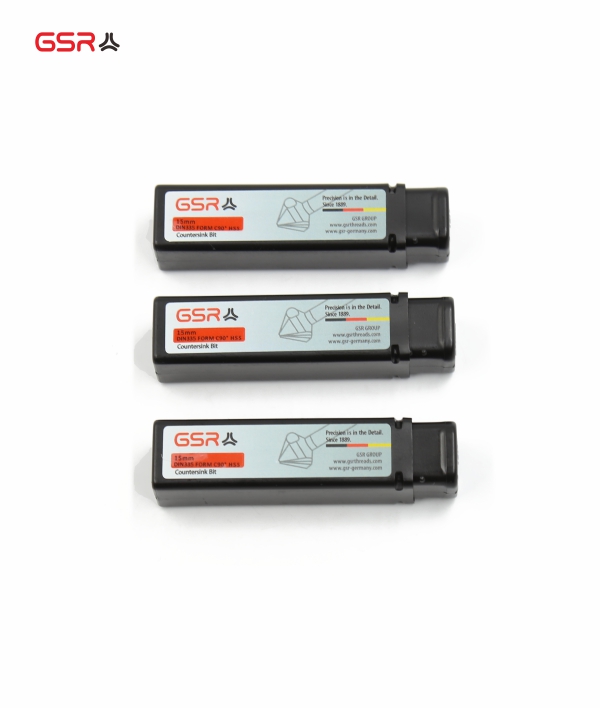
Countersink CBN-Grinded
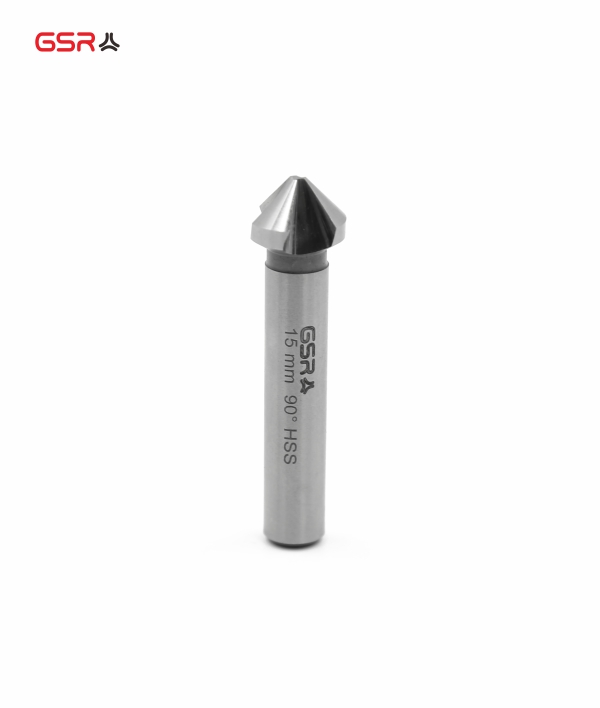
The purpose of a countersink is to allow a fastener, typically a flathead screw, to sit slightly below the surface of the spare part.
A countersink consists of a conical hole that is coaxial to a cylindrical hole, where the angle of the cone is determined by the fastener to be used.
Countersinks have a conical cutting edge geometry. The most common types are 60°, 90° and 120°. They are used for countersinking, deburring and chamfering.
Countersinks CBN-Grinded
Countersinks have a conical cutting edge geometry. The most common types are 60°, 90° and 120°. They are used for countersinking, deburring and chamfering.
Countersink parameters
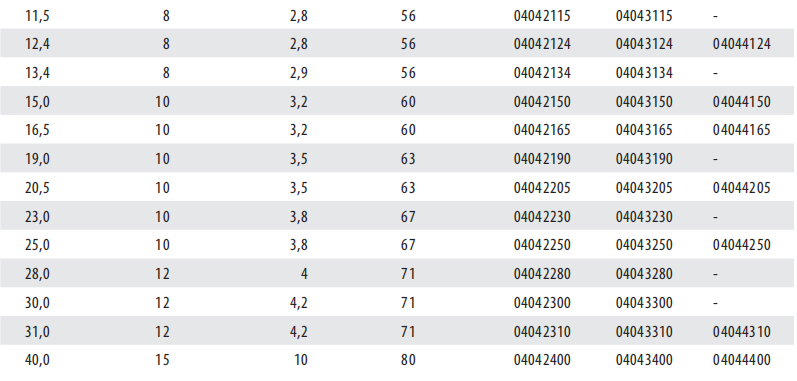
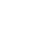
COUNTERSINKS DIN 335 C 12,4 HSS
DIN 335 = Countersinks with 3 cutting edges 90°
Form C = 3 cutting edges with cylindrical shank
12.4 mm = D1 = biggest diameter
HSS =High-speed steel
Usage of Counter-Sink
Usage HSS COUNTERSINKS
Steel, cast steel alloyed and unalloyed up to 900 N/mm² tensile strength, grey cast iron, malleable cast iron, spheroidal graphite iron, die-casting, sintered iron, nickel silver, graphite, short chip-ping aluminium alloys, brass and bronze.
Usage HSSE COUNTERSINKS
additionally usable for hot and cold work steels as well as stainless and acid-resistant steel (V2A / V4A)