Stainless Steel 304 304L 316 316L
Stainless steel, as an indispensable and important material in modern industry, is widely used in various fields due to its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Among them, 304, 304L, 316, 316L stainless steel has become a popular choice in the market due to its unique characteristics and wide range of applications. In this article, we will discuss the differences between these four types of stainless steel in detail.
I. Introduction of basic performance
304 stainless steel: 304 stainless steel is one of the most widely used stainless steel materials, with good corrosion resistance, heat resistance, low temperature strength and mechanical properties. Its stamping, bending and other hot workability is good, no heat treatment hardening phenomenon, the use of temperature range between -196 ℃ to 800 ℃. In order to maintain its corrosion resistance, 304 stainless steel must contain more than 18% chromium and more than 8% nickel. This material is resistant to corrosion in the atmosphere, but in industrial atmospheres or heavily polluted areas, it needs to be cleaned promptly to avoid corrosion.
304L Stainless Steel: As a lower carbon variant of 304 stainless steel, 304L stainless steel is similar to 304 in terms of corrosion resistance, but its lower carbon content gives it good resistance to intergranular corrosion. This characteristic allows 304L to perform better where welding is required, as the reduced carbon content avoids chromium carbide precipitation, thus reducing the risk of intergranular corrosion. In addition, 304L has good machinability and weldability, making it suitable for use in the manufacture of equipment such as chemical equipment, petroleum storage tanks and chemical reactors.
316 Stainless Steel: Compared with 304 stainless steel, 316 stainless steel has a significant improvement in corrosion resistance, atmospheric corrosion resistance and high temperature strength due to the addition of molybdenum. This material can be used in harsh conditions, such as seawater environment, chemical, dyes, paper, oxalic acid, fertiliser and other production equipment. 316 stainless steel also has good work hardening, non-magnetic, and cold rolled products have a good glossy appearance. Despite its high price, its excellent corrosion resistance makes 316 stainless steel widely used in several industries.
316L Stainless Steel: As a low carbon series of 316 steel grade, 316L stainless steel not only inherits the excellent performance of 316 stainless steel, but also has good resistance to chloride erosion and strong resistance to grain boundary corrosion. Its low carbon content design makes 316L in the high temperature environment can still maintain stable performance, will not occur intergranular corrosion phenomenon. This makes 316L stainless steel an important and indispensable material in the manufacture of marine equipment, medical devices, food processing equipment and other fields.
II. Main differences
Chemical composition
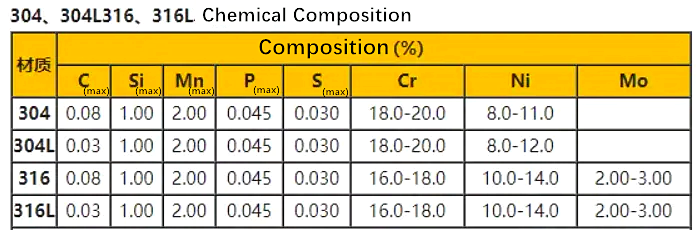
304 stainless steel: mainly contains 18%-20% chromium and 8%-10% nickel, and a small amount of carbon, silicon, manganese and other elements.
304L Stainless Steel: Compared to 304, 304L has a lower carbon content, usually below 0.03 per cent, and similar levels of other elements.
316 Stainless Steel: In addition to containing chromium and nickel similar to 304, 2-3% molybdenum has been added to improve its corrosion resistance.
316L Stainless Steel: Compared to 316, 316L has the same lower carbon content and similar levels of other elements.
2. Corrosion resistance
304 stainless steel: corrosion resistant in the atmosphere, but requires prompt cleaning in industrial atmospheres or heavily polluted areas.
304L stainless steel: corrosion resistance is similar to 304, but has better resistance to intergranular corrosion due to its low carbon content.
316 stainless steel: corrosion resistance is better than 304, especially in the environment containing chloride ions.
316L Stainless Steel: Corrosion resistance is further improved to resist chloride ions, chlorides, sulphuric acid and other chemicals.
3. Machinability
304 Stainless Steel: has good machinability and weldability and is suitable for a wide range of processing methods.
304L stainless steel: similar to 304, but its low carbon content makes better welding performance.
316 stainless steel: excellent work hardening, non-magnetic, cold rolled products with good appearance and gloss.
316L stainless steel: also has excellent processing performance, suitable for the manufacture of complex shapes and structures of the components.
4. Areas of application
304 stainless steel: widely used in food processing, storage and transport, plate heat exchangers, bellows, household goods, automotive parts, medical appliances, building materials, chemical, food industry, agriculture, ship parts and other fields.
304L stainless steel: especially suitable for equipment and parts that need good comprehensive performance (corrosion resistance and formability), such as chemical equipment, petroleum storage tanks and chemical reactors.
316 stainless steel: suitable for equipment used in seawater, chemical, dyestuff, paper, oxalic acid, fertiliser and other production equipment; photographic, food industry, coastal area facilities and other fields.
316L stainless steel: because of its excellent corrosion resistance and good processing performance, it is widely used in medical equipment, food processing equipment, building decoration and furniture manufacturing and other fields.
III. the conclusion
In summary, 304, 304L, 316, 316L stainless steel in the chemical composition, corrosion resistance, processing performance and application areas and so on there are some differences. The choice of which stainless steel material should be based on the specific use of the environment and demand for comprehensive consideration. For example, in the harsh environment containing chloride ions, 316 and 316L stainless steel because of its excellent corrosion resistance and become the first choice; and in the need to weld the occasion, 304L and 316L stainless steel is favoured because of its good welding performance. Through a deeper understanding of the differences and characteristics of these four types of stainless steel, we can better select the appropriate stainless steel materials to meet the needs of different areas.
When you need to machine internal threads on stainless steel, how to choose the right tap will have a direct impact on the machining efficiency and the quality of the threads. Therefore, understanding the properties of different stainless steels is crucial when choosing a tap to work with. If you have any questions about selecting a tap, please contact us.