NPT BSP BSPT and ZG Thread
NPT is the American National Standard Pipe Thread, which is widely used in piping systems in North America.NPT threads are characterised by good sealing and reliable connections, and are mainly used for piping connections for transporting liquids and gases.
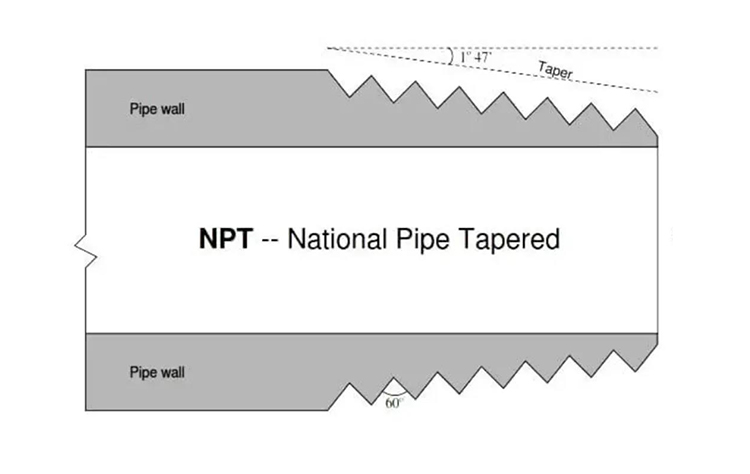
NPT Features
Taper Design: NPT threads have a 1:16 taper (i.e., 1/16" diameter change per inch), which means the threads are tapered, not straight. The tapered design helps achieve a self-sealing effect by tightening the threads to prevent leakage.
Pitch and Tooth Angle: NPT threads have a tooth angle of 60 degrees, and the pitch varies according to pipe diameter. The pitch and tooth angle are designed to ensure the strength and tightness of the threaded connection.
Standard specification: NPT thread standard specification by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) to develop, common standards are ANSI/ASME B1.20.1
Common Types
NPT: taper thread, widely used for pipe connections, sealing is achieved by the taper of the thread.
NPTF: Tapered fuel thread, similar to NPT but with higher sealing requirements, commonly used in fuel and hydraulic systems.
(NPS: Straight pipe thread, unlike NPT, has no taper and is usually used for mechanical connections that do not require a seal.)
PT thread (Pipe Thread), often called BSPT (British Standard Pipe Taper), is a kind of British Standard Pipe Thread, belongs to the tapered pipe thread.PT thread is mainly used for gas and liquid pipeline connection, with good sealing and connection strength.
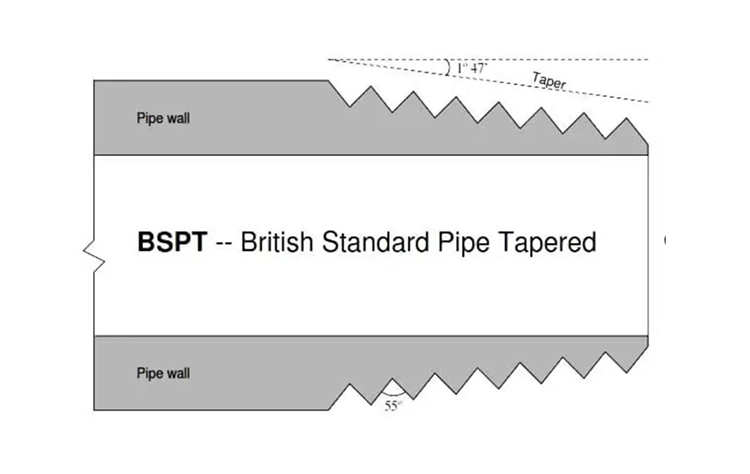
Pitch and tooth angle: PT threads have a tooth angle of 55 degrees. Pitch varies according to pipe diameter.
Standard specification: The standard for PT threads is set by the British Standards Institution (BSI), and the common standard is BS 21.
ZG thread is a kind of pipe thread in the Chinese standard, which is usually used for pipe connections that require good sealing, ZG thread has a wide range of applications in industrial and construction fields at home and abroad.
Taper design: ZG threads are tapered pipe threads with a certain degree of taper, which helps to achieve a self-sealing effect by tightening the threads to prevent leakage of liquids or gases.
Pitch and tooth angle: ZG threads have a tooth angle of 55 degrees. Pitch varies according to pipe diameter
Areas of application
Liquid and gas transport: widely used in pipeline connections for liquids and gases, such as water pipes, gas pipes and oil pipes. Taper design makes it still maintain good sealing performance under high pressure and high temperature environment.
Industrial equipment: for the connection of various industrial equipment, such as valves, pumps, instruments and pressure gauges, etc.
Buildings and infrastructure: for pipework in buildings and infrastructure to ensure safe and reliable pipework connections.
G pipe threads, also known as BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) threads, are a type of British Standard straight pipe thread. This thread is mainly used for mechanical connections and pipe connections, especially where a self-sealing effect is not required.G thread is one of the thread types in the ISO 228 standard.
Straight pipe threads: G threads are parallel threads with no taper and do not have a sealing function, and usually require the use of sealing washers, O-rings, etc. for sealing.
Pitch and Tooth Angle: G threads have a tooth angle of 55 degrees. Pitch varies according to pipe diameter.
Standards: G threads are standardised in ISO 228-1:2000 "Threaded connections and pipe connections". ISO 228 defines the dimensions, tolerances and marking of pipe threads.
Areas of application
Mechanical connections: For connections in mechanical equipment, such as hydraulic and pneumatic systems. Sealing is achieved by means of sealing gaskets or O-rings, ensuring a reliable connection.
Pipe Connections: G threads are commonly used to connect valves, fittings and other piping components in piping systems, especially those requiring high pressure sealing.
Hydraulic and pneumatic systems: Widely used in the connection of hydraulic and pneumatic systems, the use of gaskets or O-rings to achieve a seal to prevent the leakage of liquids or gases.